之前的两篇文章<<nf_ct_deliver_cached_events崩溃分析>>和<<nf_ct_deliver_cached_events崩溃修复或规避方案>>介绍了nf_conntrack模块中的一个BUG的原因和规避方案。触发BUG的原因在于NFQUEUE操作位于ipv4_conntrack_in和ipv4_confirm两个函数之间,于是本可以无中断执行完成的两个函数之间出现了CPU调度,导致大量conntrack entry冲突。各HOOK函数执行顺序如图:
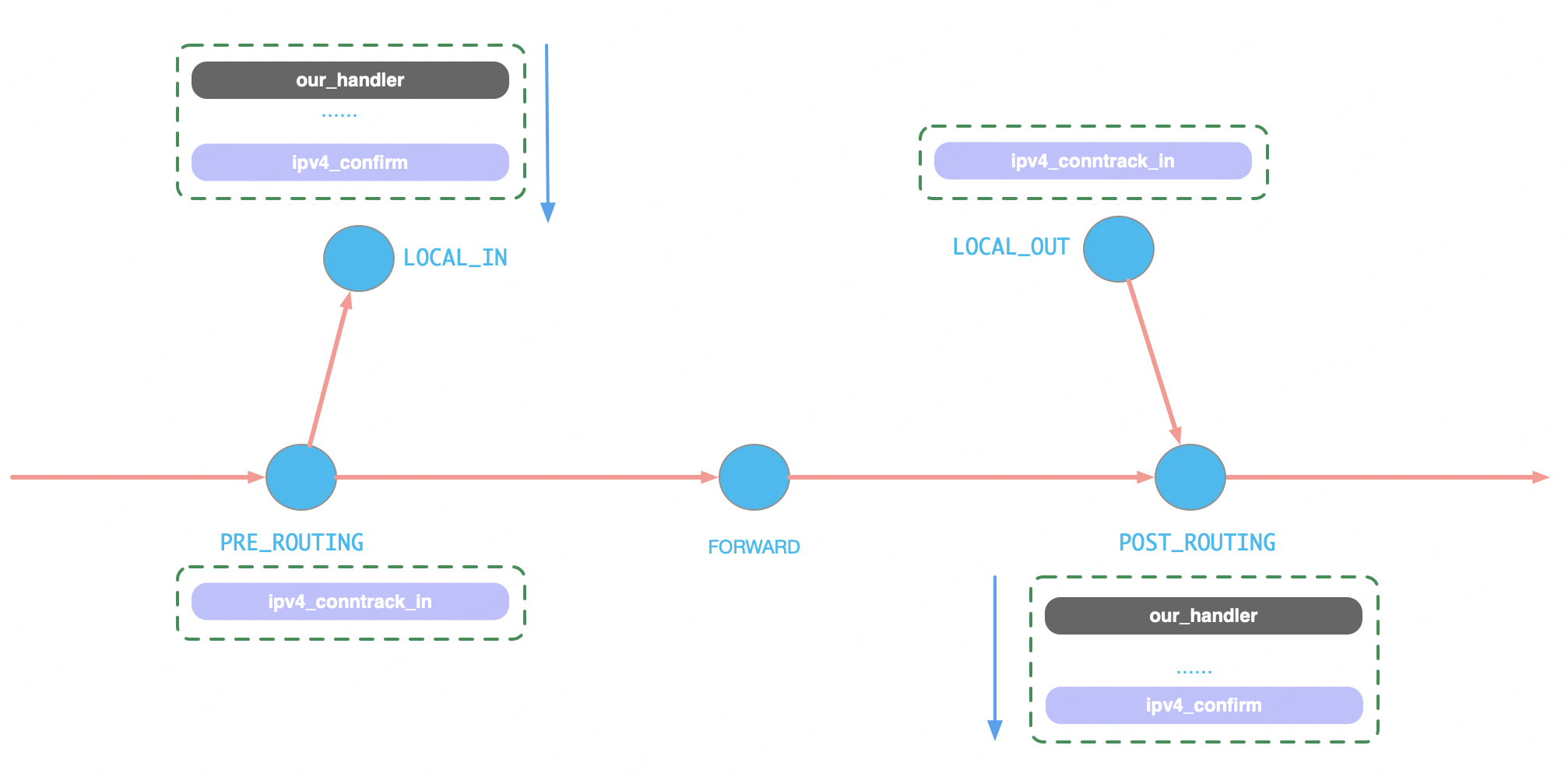
规避问题出现的思路就是将NFQUEUE操作不放在两个函数中间。之前文章中选定的思路是在我们的hook函数中提前调用ipv4_confirm。
最近,同事提出了另一个思路,就是将我们的hook函数的优先级也设置为NF_IP_PRI_LAST。因为ipv4_confirm的优先级NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM是INT_MAX, 我们的hook函数优先级也设置成INT_MAX。因为我们的内核模块依赖conntrack模块,因而conntrack模块会先于我们的内核模块先注册,从而保证我们的HOOK函数最后执行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| enum nf_ip_hook_priorities {
NF_IP_PRI_FIRST = INT_MIN,
NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_DEFRAG = -400,
NF_IP_PRI_RAW = -300,
NF_IP_PRI_SELINUX_FIRST = -225,
NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK = -200,
NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE = -150,
NF_IP_PRI_NAT_DST = -100,
NF_IP_PRI_FILTER = 0,
NF_IP_PRI_SECURITY = 50,
NF_IP_PRI_NAT_SRC = 100,
NF_IP_PRI_SELINUX_LAST = 225,
NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_HELPER = 300,
NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM = INT_MAX,
NF_IP_PRI_LAST = INT_MAX,
};
|
但这引发我思考一个问题,相同优先级的HOOK函数的先后顺序能得到保证吗?
查看CentOS7的3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64版本内核上的nf_register_hook代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| int nf_register_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
struct nf_hook_ops *elem;
int err;
err = mutex_lock_interruptible(&nf_hook_mutex);
if (err < 0)
return err;
list_for_each_entry(elem, &nf_hooks[reg->pf][reg->hooknum], list) {
if (reg->priority < elem->priority)
break;
}
list_add_rcu(®->list, elem->list.prev);
mutex_unlock(&nf_hook_mutex);
#if defined(CONFIG_JUMP_LABEL)
static_key_slow_inc(&nf_hooks_needed[reg->pf][reg->hooknum]);
#endif
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(nf_register_hook);
|
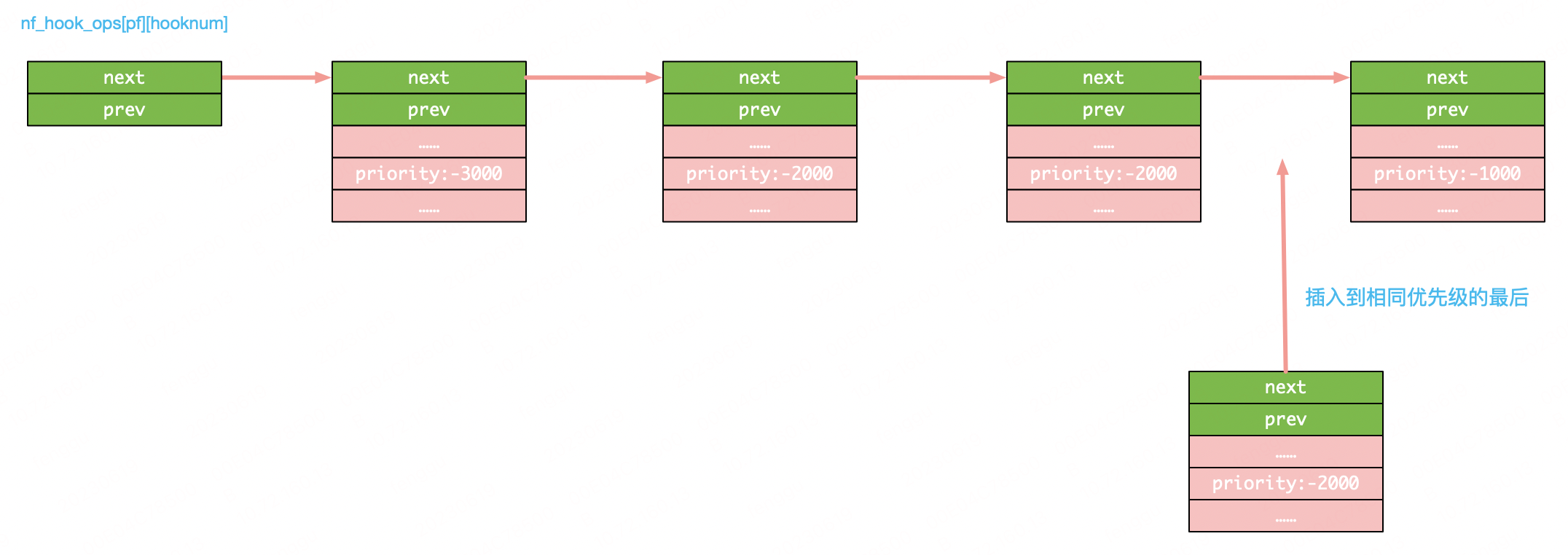
可以看到这个版本上的排序比较条件使用的是:
1
| (reg->priority < elem->priority)
|
因而,后注册的相同优先级的hook函数的确会排在先注册的相同优先级的最后位置,可以保证相同优先级的HOOK函数先注册先执行。示意图如下:
再来看CentOS8的4.18内核。函数nf_register_net_hook最终会调用到nf_hook_entries_grow函数进行排序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| static struct nf_hook_entries *
nf_hook_entries_grow(const struct nf_hook_entries *old,
const struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
unsigned int i, alloc_entries, nhooks, old_entries;
struct nf_hook_ops **orig_ops = NULL;
struct nf_hook_ops **new_ops;
struct nf_hook_entries *new;
bool inserted = false;
alloc_entries = 1;
old_entries = old ? old->num_hook_entries : 0;
if (old) {
orig_ops = nf_hook_entries_get_hook_ops(old);
for (i = 0; i < old_entries; i++) {
if (orig_ops[i] != &dummy_ops)
alloc_entries++;
}
}
if (alloc_entries > MAX_HOOK_COUNT)
return ERR_PTR(-E2BIG);
new = allocate_hook_entries_size(alloc_entries);
if (!new)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
new_ops = nf_hook_entries_get_hook_ops(new);
i = 0;
nhooks = 0;
while (i < old_entries) {
if (orig_ops[i] == &dummy_ops) {
++i;
continue;
}
if (inserted || reg->priority > orig_ops[i]->priority) {
new_ops[nhooks] = (void *)orig_ops[i];
new->hooks[nhooks] = old->hooks[i];
i++;
} else {
new_ops[nhooks] = (void *)reg;
new->hooks[nhooks].hook = reg->hook;
new->hooks[nhooks].priv = reg->priv;
inserted = true;
}
nhooks++;
}
if (!inserted) {
new_ops[nhooks] = (void *)reg;
new->hooks[nhooks].hook = reg->hook;
new->hooks[nhooks].priv = reg->priv;
}
return new;
}
|
4.18版本上最终的HOOK函数存储结构做了修改,使用的排序条件也发生了变化:
1
| reg->priority > orig_ops[i]->priority
|
这与3.10版本上的判断条件是不同的,它会导致相同优先级的后注册HOOK函数排在相同优先级的HOOK函数的最前边位置。示意图如下:
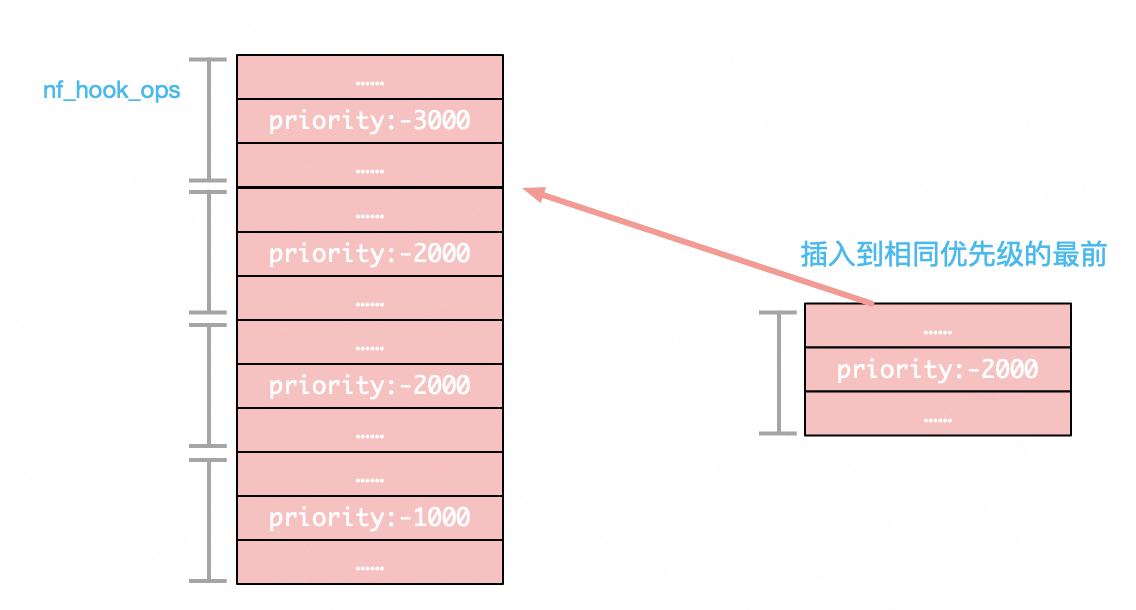
因而,相同优先级的HOOK函数先注册后执行。
可以使用如下的内核模块来进行测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
| #define pr_fmt(fmt) "[%s]: " fmt, KBUILD_MODNAME
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/version.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/skbuff.h>
#include <linux/ip.h>
#include <linux/netfilter.h>
#include <linux/netfilter_ipv4.h>
#include <net/tcp.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("nfq priority");
static unsigned int nf_hook1(void *priv,
struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct nf_hook_state *state)
{
struct iphdr *iph = ip_hdr(skb);
struct tcphdr *tcph;
u8 proto = iph->protocol;
if (proto != IPPROTO_TCP) {
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
tcph = tcp_hdr(skb);
if (ntohs(tcph->source) != 80) {
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
pr_info("HOOK: 1, TCP %d->%d\n", htons(tcph->source), htons(tcph->dest));
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
static unsigned int nf_hook2(void *priv,
struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct nf_hook_state *state)
{
struct iphdr *iph = ip_hdr(skb);
struct tcphdr *tcph;
u8 proto = iph->protocol;
if (proto != IPPROTO_TCP) {
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
tcph = tcp_hdr(skb);
if (ntohs(tcph->source) != 80) {
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
pr_info("HOOK: 2, TCP %d->%d\n", htons(tcph->source), htons(tcph->dest));
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
static struct nf_hook_ops nfhooks[] = {
{
.hook = nf_hook1,
.pf = NFPROTO_IPV4,
.hooknum = NF_INET_POST_ROUTING,
.priority = NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM,
},
{
.hook = nf_hook2,
.pf = NFPROTO_IPV4,
.hooknum = NF_INET_POST_ROUTING,
.priority = NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_CONFIRM,
},
};
int __init nfqprio_init(void)
{
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(4,13,0)
nf_register_net_hooks(&init_net, nfhooks, ARRAY_SIZE(nfhooks));
#else
nf_register_hooks(nfhooks, ARRAY_SIZE(nfhooks));
#endif
pr_info("module init\n");
return 0;
}
void __exit nfqprio_exit(void)
{
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(4,13,0)
nf_unregister_net_hooks(&init_net, nfhooks, ARRAY_SIZE(nfhooks));
#else
nf_unregister_hooks(nfhooks, ARRAY_SIZE(nfhooks));
#endif
pr_info("module exit\n");
return;
}
module_init(nfqprio_init);
module_exit(nfqprio_exit);
|
而在CentOS7上执行curl测试:
日志为:
1
2
| [29588.265123] [nfqprio]: HOOK: 1, TCP 80->28512
[29588.265280] [nfqprio]: HOOK: 2, TCP 80->28512
|
而在CentOS 8.2(4.18.0-193.el8.x86_64)上执行后的日志为:
1
2
| [8999405.679059] [nfqprio]: HOOK: 2, TCP 80->32794
[8999405.679635] [nfqprio]: HOOK: 1, TCP 80->32794
|
可以看到,在CentOS7的3.10版本内核上相同优先级的HOOK函数是先注册先执行,而在CentOS8的4.18内核上是先注册后执行。
如果只有一种内核环境,可以使用这个思路来进行规避。但对于我们的产品来说,从不同版本兼容性考虑,还是不采用这种思路,依然使用之前文章介绍的思路。


