最近CentOS7服务器上遇到一个系统崩溃:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [92957.332974] BUG: unable to handle kernel NULL pointer dereference at 0000000000000a30 [92957.332981] IP: [<ffffffffc086077d>] nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+0x2d/0x110 [nf_conntrack] ...... [92957.333112] CPU: 1 PID: 5027 Comm: Verdict3 Kdump: loaded Tainted: G OE ------------ T 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 #1 [92957.333114] Hardware name: VMware, Inc. VMware Virtual Platform/440BX Desktop Reference Platform, BIOS 6.00 12/12/2018 [92957.333116] task: ffff893cad135280 ti: ffff893c4f524000 task.ti: ffff893c4f524000 [92957.333118] RIP: 0010:[<ffffffffc086077d>] [<ffffffffc086077d>] nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+0x2d/0x110 [nf_conntrack] [92957.333125] RSP: 0018:ffff893c4f527810 EFLAGS: 00010246 [92957.333127] RAX: 0000000000000000 RBX: ffff893ca41e5140 RCX: ffffffffa035de80 [92957.333128] RDX: ffff893c4f527fd8 RSI: 0000000000000200 RDI: ffff893ca41e5140 [92957.333130] RBP: ffff893c4f527850 R08: 0000000000000000 R09: ffff893ca41e5178 [92957.333131] R10: 0000000000000001 R11: ffff893ca41e5140 R12: ffff893ca41e5140 [92957.333132] R13: ffff893c9491a500 R14: ffffffffa0367e40 R15: 0000000000000000 [92957.333135] FS: 00007fbda1d78700(0000) GS:ffff893d3fd00000(0000) knlGS:0000000000000000 [92957.333137] CS: 0010 DS: 0000 ES: 0000 CR0: 0000000080050033 [92957.333138] CR2: 0000000000000a30 CR3: 000000007fda4000 CR4: 00000000001607e0 [92957.333202] Call Trace: [92957.333221] [<ffffffffc08372ce>] ipv4_confirm+0x4e/0x100 [nf_conntrack_ipv4] [92957.333227] [<ffffffff9fc94e38>] nf_iterate+0x98/0xe0 [92957.333231] [<ffffffff9fc96240>] nf_reinject+0x160/0x1b0 [92957.333239] [<ffffffffc0a48566>] nfqnl_recv_verdict+0x216/0x310 [nfnetlink_queue] [92957.333244] [<ffffffff9f9b4716>] ? nla_parse+0xb6/0x120 [92957.333247] [<ffffffffc09b03a2>] nfnetlink_rcv_msg+0x162/0x270 [nfnetlink] [92957.333251] [<ffffffffc09b0240>] ? nfnetlink_net_exit_batch+0x70/0x70 [nfnetlink] [92957.333254] [<ffffffff9fc9249b>] netlink_rcv_skb+0xab/0xc0 [92957.333257] [<ffffffffc09b089f>] nfnetlink_rcv+0x28f/0x575 [nfnetlink] [92957.333260] [<ffffffff9fc90773>] ? __netlink_lookup+0xd3/0x130 [92957.333263] [<ffffffff9fc91e20>] netlink_unicast+0x170/0x210 [92957.333267] [<ffffffff9f99ca72>] ? memcpy_fromiovec+0x62/0xb0 [92957.333269] [<ffffffff9fc921c8>] netlink_sendmsg+0x308/0x420 [92957.333272] [<ffffffff9fc343a6>] sock_sendmsg+0xb6/0xf0 [92957.333277] [<ffffffff9fd86c8f>] ? __schedule+0x3af/0x860 [92957.333279] [<ffffffff9fc35269>] ___sys_sendmsg+0x3e9/0x400 [92957.333284] [<ffffffff9f712040>] ? futex_wake+0x90/0x180 [92957.333287] [<ffffffff9f714d2a>] ? do_futex+0x12a/0x5a0 [92957.333289] [<ffffffff9fc36921>] __sys_sendmsg+0x51/0x90 [92957.333292] [<ffffffff9fc36972>] SyS_sendmsg+0x12/0x20 [92957.333296] [<ffffffff9fd93f92>] system_call_fastpath+0x25/0x2a
使用crash工具进行分析,查看调用栈:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 crash> bt PID: 5027 TASK: ffff893cad135280 CPU: 1 COMMAND: "Verdict3" #0 [ffff893c4f527488] machine_kexec at ffffffff9f666294 #1 [ffff893c4f5274e8] __crash_kexec at ffffffff9f722562 #2 [ffff893c4f5275b8] crash_kexec at ffffffff9f722650 #3 [ffff893c4f5275d0] oops_end at ffffffff9fd8b798 #4 [ffff893c4f5275f8] no_context at ffffffff9f675d14 #5 [ffff893c4f527648] __bad_area_nosemaphore at ffffffff9f675fe2 #6 [ffff893c4f527698] bad_area at ffffffff9fd7a058 #7 [ffff893c4f5276c0] __do_page_fault at ffffffff9fd8e8b7 #8 [ffff893c4f527730] do_page_fault at ffffffff9fd8e975 #9 [ffff893c4f527760] page_fault at ffffffff9fd8a778 [exception RIP: nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+45] RIP: ffffffffc086077d RSP: ffff893c4f527810 RFLAGS: 00010246 RAX: 0000000000000000 RBX: ffff893ca41e5140 RCX: ffffffffa035de80 RDX: ffff893c4f527fd8 RSI: 0000000000000200 RDI: ffff893ca41e5140 RBP: ffff893c4f527850 R8: 0000000000000000 R9: ffff893ca41e5178 R10: 0000000000000001 R11: ffff893ca41e5140 R12: ffff893ca41e5140 R13: ffff893c9491a500 R14: ffffffffa0367e40 R15: 0000000000000000 ORIG_RAX: ffffffffffffffff CS: 0010 SS: 0018 #10 [ffff893c4f527858] ipv4_confirm at ffffffffc08372ce [nf_conntrack_ipv4] #11 [ffff893c4f527878] nf_iterate at ffffffff9fc94e38 #12 [ffff893c4f5278b8] nf_reinject at ffffffff9fc96240 #13 [ffff893c4f5278f8] nfqnl_recv_verdict at ffffffffc0a48566 [nfnetlink_queue] #14 [ffff893c4f527960] nfnetlink_rcv_msg at ffffffffc09b03a2 [nfnetlink] #15 [ffff893c4f527a60] netlink_rcv_skb at ffffffff9fc9249b #16 [ffff893c4f527a88] nfnetlink_rcv at ffffffffc09b089f [nfnetlink] #17 [ffff893c4f527b08] netlink_unicast at ffffffff9fc91e20 #18 [ffff893c4f527b50] netlink_sendmsg at ffffffff9fc921c8 #19 [ffff893c4f527bd8] sock_sendmsg at ffffffff9fc343a6 #20 [ffff893c4f527d38] ___sys_sendmsg at ffffffff9fc35269 #21 [ffff893c4f527ed0] __sys_sendmsg at ffffffff9fc36921 #22 [ffff893c4f527f40] sys_sendmsg at ffffffff9fc36972 #23 [ffff893c4f527f50] system_call_fastpath at ffffffff9fd93f92 RIP: 00007fbdac77bcbd RSP: 00007fbda1d76968 RFLAGS: 00000206 RAX: 000000000000002e RBX: 0000000000000001 RCX: 00007fbda1d76a00 RDX: 0000000000000000 RSI: 00007fbda1d76940 RDI: 0000000000000009 RBP: 00007fbda1d769d0 R8: 0000000000000008 R9: 00007fbdac0b9140 R10: fffffffffffff8c9 R11: 0000000000000293 R12: 00007fbd8c001b40 R13: 00007fbda1d769a0 R14: 0000000000000000 R15: 00000000bc0b0c00 ORIG_RAX: 000000000000002e CS: 0033 SS: 002b
可以看到崩溃点位置为:nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+45,而该函数位于nf_conntrack模块。
加载调用栈中所用到的模块:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 crash> mod -s nf_conntrack MODULE NAME SIZE OBJECT FILE ffffffffc086c960 nf_conntrack 139264 /usr/lib/debug/usr/lib/modules/3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64/kernel/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack.ko.debug crash> mod -s nf_conntrack_ipv4 MODULE NAME SIZE OBJECT FILE ffffffffc08396c0 nf_conntrack_ipv4 15053 /usr/lib/debug/usr/lib/modules/3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64/kernel/net/ipv4/netfilter/nf_conntrack_ipv4.ko.debug crash> mod -s nfnetlink_queue MODULE NAME SIZE OBJECT FILE ffffffffc0a4a080 nfnetlink_queue 18197 /usr/lib/debug/usr/lib/modules/3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64/kernel/net/netfilter/nfnetlink_queue.ko.debug crash> mod -s nfnetlink MODULE NAME SIZE OBJECT FILE ffffffffc09b2060 nfnetlink 14519 /usr/lib/debug/usr/lib/modules/3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64/kernel/net/netfilter/nfnetlink.ko.debug
反汇编nf_ct_deliver_cached_events函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 crash> dis nf_ct_deliver_cached_events 0xffffffffc0860750 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events>: nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1) [FTRACE NOP] 0xffffffffc0860755 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+5>: push %rbp 0xffffffffc0860756 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+6>: mov %rsp,%rbp 0xffffffffc0860759 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+9>: push %r14 0xffffffffc086075b <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+11>: push %r13 0xffffffffc086075d <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+13>: push %r12 0xffffffffc086075f <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+15>: push %rbx 0xffffffffc0860760 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+16>: mov %rdi,%rbx 0xffffffffc0860763 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+19>: sub $0x20,%rsp 0xffffffffc0860767 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+23>: mov %gs:0x28,%rax 0xffffffffc0860770 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+32>: mov %rax,-0x28(%rbp) 0xffffffffc0860774 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+36>: xor %eax,%eax 0xffffffffc0860776 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+38>: mov 0xf0(%rdi),%rax 0xffffffffc086077d <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+45>: mov 0xa30(%rax),%rdx 0xffffffffc0860784 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+52>: test %rdx,%rdx 0xffffffffc0860787 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+55>: je 0xffffffffc0860810 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+192> 0xffffffffc086078d <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+61>: mov 0xe8(%rdi),%rax 0xffffffffc0860794 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+68>: test %rax,%rax
可以看到崩溃点nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+45执行的指令为:
1 0xffffffffc086077d <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+45>: mov 0xa30(%rax),%rdx
而查看bt输出可以知道崩溃时%rax寄存器的值为0:
1 RAX: 0000000000000000 RBX: ffff893ca41e5140 RCX: ffffffffa035de80
指令表示从为%rax+0xa30的地址取值存入%rdx, 而0 + 0xa30的地址为0000000000000a30
1 unable to handle kernel NULL pointer dereference at 0000000000000a30
再向上查看执行的指令,%rax的值来自0xf0(%rdi):
1 0xffffffffc0860776 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+38>: mov 0xf0(%rdi),%rax
而%rdi寄存器的值为ffff893ca41e5140:
1 RDX: ffff893c4f527fd8 RSI: 0000000000000200 RDI: ffff893ca41e5140
通过指令dis -l反汇编nf_ct_deliver_cached_events函数和源码可以确认%rdi寄存器存储的结构为struct nf_conn:
1 2 /usr/src/debug/kernel-3.10.0-1160.el7/linux-3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64/include/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack.h: 144 0xffffffffc0860776 <nf_ct_deliver_cached_events+38>: mov 0xf0(%rdi),%rax
1 2 3 4 static inline struct net *nf_ct_net (const struct nf_conn *ct) { return read_pnet(&ct->ct_net); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 crash> struct -xo nf_conn struct nf_conn { [0x0] struct nf_conntrack ct_general; [0x4] spinlock_t lock; [0x8] u16 cpu; [0x10] struct nf_conntrack_tuple_hash tuplehash[2]; [0x80] unsigned long status; [0x88] struct nf_conn *master; [0x90] struct timer_list timeout; [0xe0] u_int32_t mark; [0xe4] u_int32_t secmark; [0xe8] struct nf_ct_ext *ext; [0xf0] struct net *ct_net; [0xf8] union nf_conntrack_proto proto; } SIZE: 0x138
0xf0的偏移为ct_net成员,0xf0(%rdi)是在读取struct nf_conn的ct_net成员。
查看该成员, 发现不是0:
1 2 crash> struct -x nf_conn.ct_net ffff893ca41e5140 ct_net = 0xffffffffa0315e40
再查看init_net的地址, 发现实际值和正常情况init_net的地址是匹配的:
1 2 crash> px &init_net $1 = (struct net *) 0xffffffffa0315e40
因而推测,在该CPU core上崩溃时,该结构在被其他cpu core使用写成了正常值。
阅读源码知道,nf_conn结构是从SLAB内存中分配的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 net->ct.slabname = kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "nf_conntrack_%llu" , (u64)atomic64_inc_return(&unique_id)); if (!net->ct.slabname) goto err_slabname; net->ct.nf_conntrack_cachep = kmem_cache_create(net->ct.slabname, sizeof (struct nf_conn), 0 , SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU, NULL );
而重用该结构时,会调用__nf_conntrack_alloc函数, 该函数会将struct nf_conn结构的成员变量tuplehash之后的status和proto之间的位置置为0,而ct_net正好位于该区间。之后会再次初始化ct_net为正常的net值:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 ct = kmem_cache_alloc(net->ct.nf_conntrack_cachep, gfp); if (ct == NULL ) goto out; memset (&ct->tuplehash[IP_CT_DIR_MAX], 0 , offsetof(struct nf_conn, proto) - offsetof(struct nf_conn, tuplehash[IP_CT_DIR_MAX])); spin_lock_init(&ct->lock); ct->tuplehash[IP_CT_DIR_ORIGINAL].tuple = *orig; ct->tuplehash[IP_CT_DIR_ORIGINAL].hnnode.pprev = NULL ; ct->tuplehash[IP_CT_DIR_REPLY].tuple = *repl; *(unsigned long *)(&ct->tuplehash[IP_CT_DIR_REPLY].hnnode.pprev) = hash; setup_timer(&ct->timeout, death_by_timeout, (unsigned long )ct); write_pnet(&ct->ct_net, net);
也就是说,如果一个CPU core正常分配该struct nf_conn结构执行到将memset操作,而另一个CPU core上恰好执行读取ct_net的操作,就会读取NULL值。因而推测崩溃发生时,这个struct nf_conn结构已经在另一个CPU core上被重用。
接下来开始分析崩溃时,sk_buff数据包内容来分析当时的流量。最后崩溃时的寄存器和栈中并没有相应sk_buff的地址,因而需要在层层栈桢中去追溯sk_buff的地址。因为x86_64体系结构上在前6个参数都是通过寄存器(参数从左到右放入寄存器:rdi, rsi, rdx, rcx, r8, r9)进行传参,因而找某个局部变量并不是非常简单。从vmcore文件中分析栈中局部变量可以参考这篇文章:
文章中提到的主要思路就是依赖变量和%rbp寄存器的关系进行查找。因为栈上的变量一般都是以%rbp为基址进行表示,如0xf0(%rbp)。而每次函数调用时都会将之前的%rbp寄存器进行压栈。我们找到相应栈桢%rbp的值,再根据变量的偏移量就可以找到相应的内存地址。
关于栈桢可以参考这篇文章:
我这里补充一种思路,就是根据函数中使用的某个寄存器来查找。当某个寄存器在本级函数使用,在下级函数中也使用到,因为内容有被污染,因而需要在函数头部压栈进行保存,返回前再出栈恢复内容。
在这个崩溃栈中,nf_reinject调用了nf_iterate。
反汇编nf_reinject:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0xffffffff9fc96210 <nf_reinject+304>: lea 0x28(%rbx),%r14 0xffffffff9fc96214 <nf_reinject+308>: movl $0x80000000,0x34(%rbx) 0xffffffff9fc9621b <nf_reinject+315>: movzbl 0x38(%rbx),%edx 0xffffffff9fc9621f <nf_reinject+319>: mov 0x30(%rbx),%eax 0xffffffff9fc96222 <nf_reinject+322>: lea -0x30(%rbp),%rcx 0xffffffff9fc96226 <nf_reinject+326>: mov %r13,%rsi 0xffffffff9fc96229 <nf_reinject+329>: lea (%rax,%rdx,8),%rdi 0xffffffff9fc9622d <nf_reinject+333>: mov %r14,%rdx 0xffffffff9fc96230 <nf_reinject+336>: shl $0x4,%rdi 0xffffffff9fc96234 <nf_reinject+340>: add $0xffffffffa0367d00,%rdi 0xffffffff9fc9623b <nf_reinject+347>: callq 0xffffffff9fc94da0 <nf_iterate>
nf_iterate原型为:
1 2 3 4 unsigned int nf_iterate (struct list_head *head, struct sk_buff *skb, struct nf_hook_state *state, struct nf_hook_ops **elemp)
第二个参数为sk_buff, 而第二个参数使用%rsi寄存器传递, 根据前边执行的指令:
1 0xffffffff9fc96226 <nf_reinject+326>: mov %r13,%rsi
可以知道%r13中的值就是sk_buff的地址。
反汇编nf_iterate函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 0xffffffff9fc94da0 <nf_iterate>: nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1) [FTRACE NOP] 0xffffffff9fc94da5 <nf_iterate+5>: push %rbp 0xffffffff9fc94da6 <nf_iterate+6>: mov %rsp,%rbp 0xffffffff9fc94da9 <nf_iterate+9>: push %r14 0xffffffff9fc94dab <nf_iterate+11>: mov %rdi,%r14 0xffffffff9fc94dae <nf_iterate+14>: push %r13 0xffffffff9fc94db0 <nf_iterate+16>: mov %rsi,%r13 0xffffffff9fc94db3 <nf_iterate+19>: push %r12 0xffffffff9fc94db5 <nf_iterate+21>: mov %rcx,%r12 0xffffffff9fc94db8 <nf_iterate+24>: push %rbx 0xffffffff9fc94db9 <nf_iterate+25>: mov %rdx,%rbx 0xffffffff9fc94dbc <nf_iterate+28>: sub $0x10,%rsp
可以看到在nf_iterate函数头部对%r13进行了压栈,因为顺序为:
1 2 3 push rbp push r14 push r13
因而%r13的位置就是比rbp低16字节的位置。
再使用bt -Fsf查看函数栈桢:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 #11 [ffff893c4f527878] nf_iterate+152 at ffffffff9fc94e38 ffff893c4f527880: ipv4_conntrack_ops+288 0000000008d72c81 ffff893c4f527890: [kmalloc-128] 0000000000000001 ffff893c4f5278a0: [kmalloc-256] [kmalloc-128] ffff893c4f5278b0: ffff893c4f5278f0 nf_reinject+352 #12 [ffff893c4f5278b8] nf_reinject+352 at ffffffff9fc96240 ffff893c4f5278c0: ipv4_conntrack_ops+288 0000000008d72c81 ffff893c4f5278d0: ffff893c4f527968 0000000000000001 ffff893c4f5278e0: [kmalloc-96] [kmalloc-128] ffff893c4f5278f0: ffff893c4f527958 nfqnl_recv_verdict+534
nf_reinject的返回地址nf_reinject+352位于ffff893c4f5278b8, 因而%r13被压栈在ffff893c4f5278a0。
读取内容:
1 2 crash> rd ffff893c4f5278a0 ffff893c4f5278a0: ffff893c9491a500 ....<...
因而sk_buff的地址为:ffff893c9491a500。
通过设备名称校验一下地址是否正确:
1 2 3 4 crash> struct sk_buff.dev ffff893c9491a500 dev = 0xffff893c358b8000 crash> struct net_device.name 0xffff893c358b8000 name = "ens192\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000"
设备名称ens192正常,地址应该正确。
查看sk_buff关联的struct nf_conn结构:
1 2 crash> struct sk_buff.nfct ffff893c9491a500 nfct = 0xffff893c7fc96b40
发现sk_buff关联的nf_conn为0xffff893c7fc96b40, 这和崩溃时的ffff893ca41e5140并不一致。
很令人疑惑,怀疑在调用过程中有地方修改了sk_buff.nfct的值。
通过查看源码,发现调用链上的确有一处地方进行了修改。
nf_conntrack_confirm函数会调用nf_ct_deliver_cached_events函数,传递的参数ct是在函数开始时就已经从sk_buff中通过skb_nfct取出的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 static inline int nf_conntrack_confirm (struct sk_buff *skb) { struct nf_conn *ct =struct nf_conn *)skb_nfct(skb); int ret = NF_ACCEPT; if (ct && !nf_ct_is_untracked(ct)) { if (!nf_ct_is_confirmed(ct)) ret = __nf_conntrack_confirm(skb); if (likely(ret == NF_ACCEPT)) nf_ct_deliver_cached_events(ct); } return ret; }
而__nf_conntrack_confirm函数可能会调用nf_ct_resolve_clash修改sk_buff.nfct。
如果是这种情况发生的话,我们在vmcore文件中看到的sk_buff.nfct是已经修改后的值,而崩溃时的ct值则为修改之前的值。应该是之前的struct nf_conn结构被复用恰好出现前边分析的情况引发崩溃。
查看内核社区这里的代码,发现不久前社区修改了这里:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 netfilter: conntrack: re-fetch conntrack after insertion In case the conntrack is clashing, insertion can free skb->_nfct and set skb->_nfct to the already-confirmed entry. This wasn't found before because the conntrack entry and the extension space used to free'd after an rcu grace period, plus the race needs events enabled to trigger.
感觉看到了希望,大概率就是这里的问题。但社区commit里没有提到这会引发崩溃。因而还在怀疑是否是我们的内核模块额外有其他影响才会引发崩溃。
在Google搜索找到一个相同的崩溃:
它的情况是关闭了Suricata之后崩溃不再复现了。Suricata使用NFQUEUE机制往用户态上送数据包。我们的业务模块也使用NFQUEUE机制将数据包送到用户态进行分析然后再将裁决结果返回给内核进行放行。完全一致的机制,因而怀疑崩溃发生和NFQUEUE机制有关系。
接下来就要分析什么场景下会导致崩溃,这需要对conntrack实现有所了解。
conntrack具体实现可以参考这两篇文章,写的非常详细:
sk_buff结构关联struct nf_conn结构是根据从sk_buff中获取的tuple信息从全局的哈希表中进行查找,而struct nf_conn结构从创建到插入哈希表分为两步:
在PRE_ROUTING和LOCAL_OUT阶段,主要是调用ipv4_conntrack_in函数根据tuple从全局哈希表中查找是否已经有相应的struct nf_conn结构。如果没有,会创建一个struct nf_conn结构插入unconfirmed list链表结构。
在LOCAL_IN和POST_ROUTING阶段,调用ipv4_confirm函数将struct nf_conn结构从unconfirmed list链表中插入到哈希表。
在第二个阶段,在将struct nf_conn结构插入哈希表前还要在哈希表进行查找是否已有相同tuple信息的结构。如果已有,则说明相同的conntrack有了两个nf_conn结构,需要处理这种冲突,具体的实现就是函数nf_ct_resolve_clash:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 static int nf_ct_resolve_clash (struct net *net, struct sk_buff *skb, enum ip_conntrack_info ctinfo, struct nf_conntrack_tuple_hash *h) { struct nf_conn *ct = const struct nf_conntrack_l4proto *l4proto ; enum ip_conntrack_info oldinfo ; struct nf_conn *loser_ct = l4proto = __nf_ct_l4proto_find(nf_ct_l3num(ct), nf_ct_protonum(ct)); if (l4proto->allow_clash && !nf_ct_is_dying(ct) && atomic_inc_not_zero(&ct->ct_general.use)) { if (((ct->status & IPS_NAT_DONE_MASK) == 0 ) || nf_ct_match(ct, loser_ct)) { nf_ct_acct_merge(ct, ctinfo, loser_ct); nf_conntrack_put(&loser_ct->ct_general); nf_ct_set(skb, ct, oldinfo); return NF_ACCEPT; } nf_ct_put(ct); } NF_CT_STAT_INC(net, drop); return NF_DROP; }
处理的过程就是先调用nf_conntrack_put, 然后将sk_buff.nfct指向之前已经在哈希表中的nf_conn结构。
后插入的这个nf_conn结构,源码中叫做loser_ct。loser_ct因为只有这一个sk_buff在关联,因而引用计数为1, 在函数nf_conntrack_put中引用计数减1后变为0, 从而调用nf_conntrack_destroy(nfct)销毁了nf_conn结构:
1 2 3 4 5 6 void nf_conntrack_destroy (struct nf_conntrack *nfct) ;static inline void nf_conntrack_put (struct nf_conntrack *nfct) { if (nfct && atomic_dec_and_test(&nfct->use)) nf_conntrack_destroy(nfct); }
因而推论更进一步,当发生conntrack冲突时,loser_ct在一个CPU core被释放,而另一个CPU core上复用该nf_conn结构执行到memset的操作。而释放loser_ct的CPU core执行到nf_ct_deliver_cached_events中的nf_ct_net读取nf_conn.ct_net,读取到NULL值。
1 2 3 4 5 void nf_ct_deliver_cached_events (struct nf_conn *ct) { struct net *net =
官方修复中提到:
1 2 3 This wasn't found before because the conntrack entry and the extension space used to free'd after an rcu grace period, plus the race needs events enabled to trigger.
conntrack entry(就是struct nf_conn)的释放会被推迟一个rcu grace period。
看上去有点像说明因为SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU选项,所以在rcu grace period内结构不会被复用。但我对这里有些不同的理解。conntrack entry的SLAB创建时指定了选项SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU, 但这个选项的作用是推迟SLAB内存页释放,而不是推迟object释放。include/linux/slab.h中的注释明确表示object一旦调用kmem_cache_free(),在一个rcu grace period内可以看到object被重用:
另一个影响崩溃触发可能性的因素是,从nf_ct_resolve_clash()返回到执行nf_ct_deliver_cached_events的时间差和另一个CPU core重用该nf_conn结构的时间谁快谁慢的问题。
感觉上nf_ct_resolve_clash返回到执行nf_ct_deliver_cached_events应该更快,不太能构成上述的推论条件。
但查看源码发现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 out: nf_ct_add_to_dying_list(ct); ret = nf_ct_resolve_clash(net, skb, ctinfo, h); dying: nf_conntrack_double_unlock(hash, reply_hash); NF_CT_STAT_INC(net, insert_failed); local_bh_enable(); return ret;
nf_ct_resolve_clash返回后__nf_conntrack_confirm函数会调用local_bh_enable, 这会开启软中断,处理软中断的过程会延迟这个CPU core调用nf_ct_deliver_cached_events的时间。
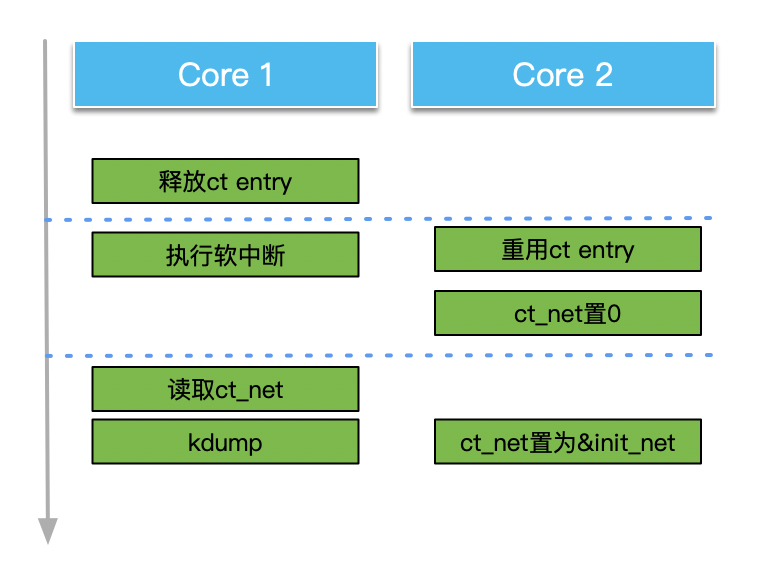
这样,推论就进一步完整了: 当发生conntrack冲突时,loser_ct在一个CPU core被释放,这时开启并执行软中断延迟一段时间,而另一个CPU core上复用该nf_conn结构执行到memset的操作。而释放loser_ct的CPU core执行到nf_ct_deliver_cached_events中的nf_ct_net读取nf_conn.ct_net,读取到NULL值,引发崩溃,如下图:
这时还有一个疑惑,就是conntrack冲突的产生。之前的文章<<NFQUEUE机制导致DNS请求5秒超时分析>> 分析过这个过程。我们的业务逻辑函数运行在LOCAL_IN和POST_ROUTING的最开始执行位置,而ipv4_confirm注册在最后执行的位置。在我们的逻辑里通过NFQUEUE机制上送数据包。在没有我们这个逻辑的场景下,netfilter会直接运行完上述的两个步骤。而我们的NFQUEUE位于两个步骤之间,第一个包创建nf_conn结构并放入unconfirmed list之后被上送用户态。这时第二个包到达,因为第一个包还没有执行confirm过程,全局哈希表中是没有这个nf_conn结构的,因而会再创建一个nf_conn,这样就产生了conntrack冲突。
当然这种过程适用于UDP,而不适用于TCP,因为TCP第二个包发送要等第一个包的响应。
我们再次确认一下nf_conn和sk_buff中的数据信息。
从nf_conn中可以看协议为UDP(0x11):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 crash> struct -x nf_conn.tuplehash[0].tuple.dst 0xffff893c7fc96b40 tuplehash[0].tuple.dst = { u3 = { all = {0x733b4c0a, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0}, ip = 0x733b4c0a, ip6 = {0x733b4c0a, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0}, in = { s_addr = 0x733b4c0a }, in6 = { in6_u = { u6_addr8 = "\nL;s\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000", u6_addr16 = {0x4c0a, 0x733b, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0}, u6_addr32 = {0x733b4c0a, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0} } } }, u = { all = 0xb512, tcp = { port = 0xb512 }, udp = { port = 0xb512 }, icmp = { type = 0x12, code = 0xb5 }, dccp = { port = 0xb512 }, sctp = { port = 0xb512 }, gre = { key = 0xb512 } }, protonum = 0x11, dir = 0x0 }
查看sk_buff结构也可以确认协议为UDP(0x11):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 crash> struct -x sk_buff.network_header ffff893c9491a500 network_header = 0xaa crash> struct -x sk_buff.head ffff893c9491a500 head = 0xffff893c80fd1400 "" crash> px (0xffff893c80fd1400 + 0xaa) $2 = 0xffff893c80fd14aa crash> struct -x iphdr 0xffff893c80fd14aa struct iphdr { ihl = 0x5, version = 0x4, tos = 0x0, tot_len = 0x6600, id = 0x2097, frag_off = 0x0, ttl = 0x40, protocol = 0x11, check = 0xbe57, saddr = 0x9e3b4c0a, daddr = 0x733b4c0a }
conntrack冲突可以通过systemtap来进行确认,脚本内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 %{ #include <net/udp.h> %} probe module ("nf_conntrack" ) .function ("nf_ct_resolve_clash" ) { iphdr = __get_skb_iphdr($skb) saddr = format_ipaddr(__ip_skb_saddr(iphdr), %{ AF_INET %}) daddr = format_ipaddr(__ip_skb_daddr(iphdr), %{ AF_INET %}) protocol = __ip_skb_proto(iphdr) udphdr = __get_skb_tcphdr($skb) if (protocol == %{ IPPROTO_UDP %}) { dport = __tcp_skb_dport(udphdr) sport = __tcp_skb_sport(udphdr) printf ("nf_ct_resolve_clash: %s:%d->%s:%d, ct: %p, ctinfo: %d, mark: %x\n" , saddr, sport, daddr, dport, $skb->nfct, $skb->nfctinfo, $skb->mark) } }
至此可以确认该崩溃发生的三个核心要素:nf_conntrack_confirm函数中的BUG存在conntrack冲突大量发生,这是由于在conntrack两步骤之间的NFQUEUE机制导致nf_ct_resolve_clash和nf_ct_deliver_cached_events之间的软中断处理时延。这可以在网卡大量处理发包时发生。
截止到写作之时,当前CentOS7最新的内核版本是2022-05-19发布的3.10.0-1160.66.1.el7, 还没有包含这个BUG的修复, 不知道Redhat官方是否会修复这个问题。
我们自己解决这个问题可以修复代码后,重新编译nf_conntrack模块进行替换。
参考链接: