Kubernetes没有给本地环境(Bare-metal, On-Premise)提供负载均衡实现,LoadBalancer类型的服务主要在各大公有云厂商上能够得到原生支持。在本地环境创建LoadBalancer类型的服务后,服务的EXTERNAL-IP会一直处于<pending>状态。这是因为在本地环境没有相应的controller来处理这些LoadBalancer服务。比如:
1
2
3
4
| [root@master1 vagrant]
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.32.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 31d
whoami LoadBalancer 10.32.0.132 <pending> 80:31620/TCP 103s
|
之前的文章<<基于LVS DR模式的Kubernetes Service External-IP实现>>介绍了手动设置EXTERNAL-IP的方式实现外部负载均衡。本文通过在本地环境实现一个简单的controller来处理LoadBalancer类型服务自动实现负载均衡器。架构示意如图:
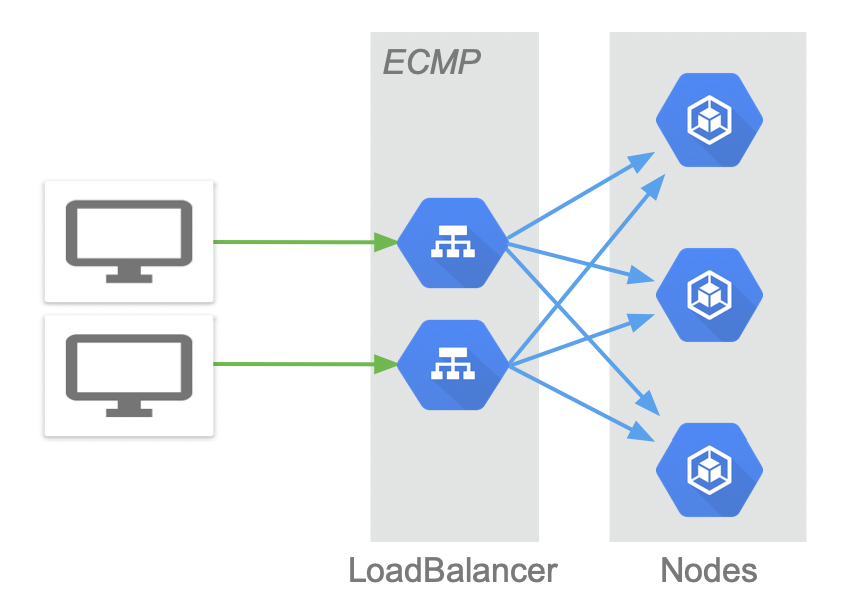
LoadBalancer是位于Kubernetes集群外的独立集群。可以通过ECMP将请求分散到不同的LoaderBalancer节点上,LoadBalancer再将请求分发到Kubernetes的node上。
服务依然使用之前文章中的whoami服务定义,type修改为LoadBalancer:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: whoami
name: whoami
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: whoami
type: LoadBalancer
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: whoami
labels:
app: whoami
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: whoami
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: whoami
spec:
containers:
- name: whoami
image: containous/whoami:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
|
创建服务:
1
2
3
| [root@master1 vagrant]
service/whoami created
deployment.apps/whoami created
|
此时查看集群中的service, 可以看到whoami服务的EXTERNAL-IP处于<pending>状态:
1
2
3
4
| [root@master1 vagrant]
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.32.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 31d <none>
whoami LoadBalancer 10.32.0.188 <pending> 80:31220/TCP 6s app=whoami
|
接着编写自定义的controller来处理LoadBalancer, 自定义controller的编写可以参考之前的文章<<Kubernetes CDR和Custom Controller>>, main.py源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
|
import logging
import sys
import os
from kubernetes import client, config, watch
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
out_hdlr = logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)
out_hdlr.setFormatter(logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s %(message)s'))
out_hdlr.setLevel(logging.INFO)
log.addHandler(out_hdlr)
log.setLevel(logging.INFO)
lb_ip_pools = [
'10.240.0.210',
'10.240.0.211',
'10.240.0.212',
'10.240.0.213',
'10.240.0.214',
'10.240.0.215'
]
node_ips = ['10.240.0.101', '10.240.0.102']
lb_services = {}
kubernetes_services = {}
def add_services(svc_manifest):
ports = svc_manifest.spec.ports
lb_svcs = []
for ip in lb_ip_pools:
if (ip not in lb_services) or (len(lb_services[ip]) == 0):
lb_services[ip] = {}
for port in ports:
lb_svcs.append((port.protocol, ip, port.port))
if port.port not in lb_services[ip]:
lb_services[ip][port.port] = []
lb_services[ip][port.port].append(port.protocol)
kubernetes_services[svc_manifest.metadata.name] = lb_svcs
return lb_svcs
valid_ip = True
for port in ports:
if port.port in lb_services[ip]:
valid_ip = False
break
if valid_ip:
for port in ports:
lb_svcs.append((port.protocol, ip, port.port))
if port.port not in lb_services[ip]:
lb_services[ip][port.port] = []
lb_services[ip][port.port].append(port.protocol)
kubernetes_services[svc_manifest.metadata.name] = lb_svcs
return lb_svcs
return None
def del_services(svc_manifest):
lb_svcs = kubernetes_services[svc_manifest.metadata.name]
del kubernetes_services[svc_manifest.metadata.name]
for svc in lb_svcs:
del lb_services[svc[1]][svc[2]]
return lb_svcs
def del_ipvs(lb_svcs):
for item in lb_svcs:
if item[0] == 'TCP':
command = "ipvsadm -D -t %s:%d" % (item[1], item[2])
os.system(command)
elif item[0] == 'UDP':
command = "ipvsadm -D -u %s:%d" % (item[1], item[2])
os.system(command)
def add_ipvs(lb_svcs):
for item in lb_svcs:
if item[0] == 'TCP':
command = "ipvsadm -A -t %s:%d -s rr" % (item[1], item[2])
os.system(command)
for node_ip in node_ips:
command = "ipvsadm -a -t %s:%d -r %s -g" % (item[1], item[2], node_ip)
os.system(command)
elif item[0] == 'UDP':
command = "ipvsadm -A -u %s:%d -s rr" % (item[1], item[2])
os.system(command)
for node_ip in node_ips:
command = "ipvsadm -a -u %s:%d -r %s -g" % (item[1], item[2], node_ip)
os.system(command)
else:
log.error("invalid protocol: %s", item[0])
def main():
config.load_kube_config()
v1 = client.CoreV1Api()
w = watch.Watch()
for item in w.stream(v1.list_service_for_all_namespaces):
if item["type"] == "ADDED":
svc_manifest = item['object']
namespace = svc_manifest.metadata.namespace
name = svc_manifest.metadata.name
svc_type = svc_manifest.spec.type
log.info("Service ADDED: %s %s %s" % (namespace, name, svc_type))
if svc_type == "LoadBalancer":
if svc_manifest.status.load_balancer.ingress == None:
log.info("Process load balancer service add event")
lb_svcs = add_services(svc_manifest)
if lb_svcs == None:
log.error("no available loadbalancer IP")
continue
add_ipvs(lb_svcs)
svc_manifest.status.load_balancer.ingress = [{'ip': lb_svcs[0][1]}]
v1.patch_namespaced_service_status(name, namespace, svc_manifest)
log.info("Update service status")
elif item["type"] == "MODIFIED":
log.info("Service MODIFIED: %s %s" % (item['object'].metadata.name, item['object'].spec.type))
elif item["type"] == "DELETED":
svc_manifest = item['object']
namespace = svc_manifest.metadata.namespace
name = svc_manifest.metadata.name
svc_type = svc_manifest.spec.type
log.info("Service DELETED: %s %s %s" % (namespace, name, svc_type))
if svc_type == "LoadBalancer":
if svc_manifest.status.load_balancer.ingress != None:
log.info("Process load balancer service delete event")
lb_svcs = del_services(svc_manifest)
if len(lb_svcs) != 0:
del_ipvs(lb_svcs)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
|
我们的controller程序通过Kubernetes APIServer监控service对象。当检测到有LoadBalancer类型的service创建后,则分配VIP并在节点上创建IPVS服务,然后修改相应service的status。我们使用的依然是RR模式,将数据包分发到后端的node。修改目的MAC地址的数据包到达node能够正常处理是由于kube-proxy会根据修改后的service对象创建相应的iptables规则:
1
| -A KUBE-SERVICES -d 10.240.0.210/32 -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/whoami:web loadbalancer IP" -m tcp --dport 80 -j KUBE-FW-225DYIB7Z2N6SCOU
|
我们的实验环境是单节点的IPVS, 为了简单直接在IPVS节点上运行我们的controller,因而不存在多次修改service状态的问题。如果在多节点的IPVS集群,controller可以通过Puppet,SaltStack或者Ansible等运维部署工具创建IPVS服务。
在IPVS节点上安装依赖的kubernetes库, 因为我们使用的kubernetes版本为1.15.3, 因而安装11.0.0版本, 具体版本依赖参考官网说明
1
| pip3 install kubernetes==11.0.0
|
运行我们的controller:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| [root@lb1 ipvslb]
2021-11-21 04:18:25,018 Service ADDED: default kubernetes ClusterIP
2021-11-21 04:18:25,019 Service ADDED: default whoami LoadBalancer
2021-11-21 04:18:25,019 Process load balancer service add event
2021-11-21 04:18:25,064 Update service status
2021-11-21 04:18:25,066 Service MODIFIED: whoami LoadBalancer
|
此时再去查看service:
1
2
3
4
| [root@master1 vagrant]
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.32.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 31d
whoami LoadBalancer 10.32.0.132 10.240.0.210 80:31620/TCP 2m40s
|
可以看到whoami服务的EXTERNAL-IP获取到了分配的VIP: 10.240.0.210。查看IPVS服务, 也可以看到对应的服务已经建立:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| [root@lb1 ipvslb]
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 10.240.0.210:80 rr
-> 10.240.0.101:80 Route 1 0 0
-> 10.240.0.102:80 Route 1 0 0
|
此时去访问VIP, 访问成功:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| [root@master1 vagrant]
Hostname: whoami-6756777fd4-4lpvl
IP: 127.0.0.1
IP: ::1
IP: 10.230.64.2
IP: fe80::ec48:94ff:fea0:db31
RemoteAddr: 10.230.10.0:45298
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.240.0.210
User-Agent: curl/7.29.0
Accept: */*
[root@master1 vagrant]
Hostname: whoami-6756777fd4-qzm6r
IP: 127.0.0.1
IP: ::1
IP: 10.230.10.19
IP: fe80::60b7:2aff:feab:68c2
RemoteAddr: 10.230.64.0:45304
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.240.0.210
User-Agent: curl/7.29.0
Accept: */*
|
接着删除whoami服务:
1
2
| [root@master1 vagrant]
service "whoami" deleted
|
从controller输出可以看到事件被正确处理:
1
2
| 2021-11-21 04:27:34,046 Service DELETED: default whoami LoadBalancer
2021-11-21 04:27:34,047 Process load balancer service delete event
|
查看IPVS服务, 也被正确删除了:
1
2
3
4
| [root@lb1 ipvslb]
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
|
在我们的示例中,VIP池中的IP需要提前在IPVS节点配置好,比如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| [root@lb1 ipvslb]
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:48:90:6c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.240.0.6/24 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.240.0.201/32 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.240.0.210/32 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.240.0.211/32 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.240.0.212/32 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.240.0.213/32 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.240.0.214/32 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.240.0.215/32 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe48:906c/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
|
node的IP也是在代码里提前配置的,正常应该从Kubernetess APIServer获取。在示例里简单处理了。
metallb是当前使用范围较广的本地环境LoadBalancer实现,它本身没有使用外部独立的负载均衡集群,是在node节点上实现的负载均衡功能。很多Kubernetes产品已经集成了它,后续有时间可以分析一下它的源码实现。
参考:
